Gynaecological cancers refer to cancers that arise in a woman’s reproductive organs. The most common include:
Less commonly, they may affect:
Cervical cancer is the second most common cancer in Indian women after breast cancer. Uterine cancers are typically seen in elderly and obese women. Ovarian cancers can occur in both younger women and those in the reproductive age group.
Good news: Most of these cancers are curable when detected early. With advancements in treatment, even advanced-stage cancers are now treatable with excellent outcomes.
Any vaginal bleeding outside your normal periods or post-menopause must be evaluated.
Early-stage (less than 4 cm): Primary surgery
Locally advanced: Chemotherapy + Radiotherapy, followed by surgery if residual disease
Modern protocols recommend neoadjuvant chemotherapy before radiation (INTERLACE trial)
Surgery first is the standard (removal of uterus and ovaries with or without lymph nodes)
Followed by radiotherapy or chemotherapy depending on pathology
Early-stage: Primary surgery
Advanced-stage:
3–4 cycles of chemotherapy
Then comprehensive cytoreductive surgery (removal of ovaries, uterus, peritoneum, and involved bowel segments)
May be followed by HIPEC (Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy), which significantly improves survival (OV-HIPEC trial)
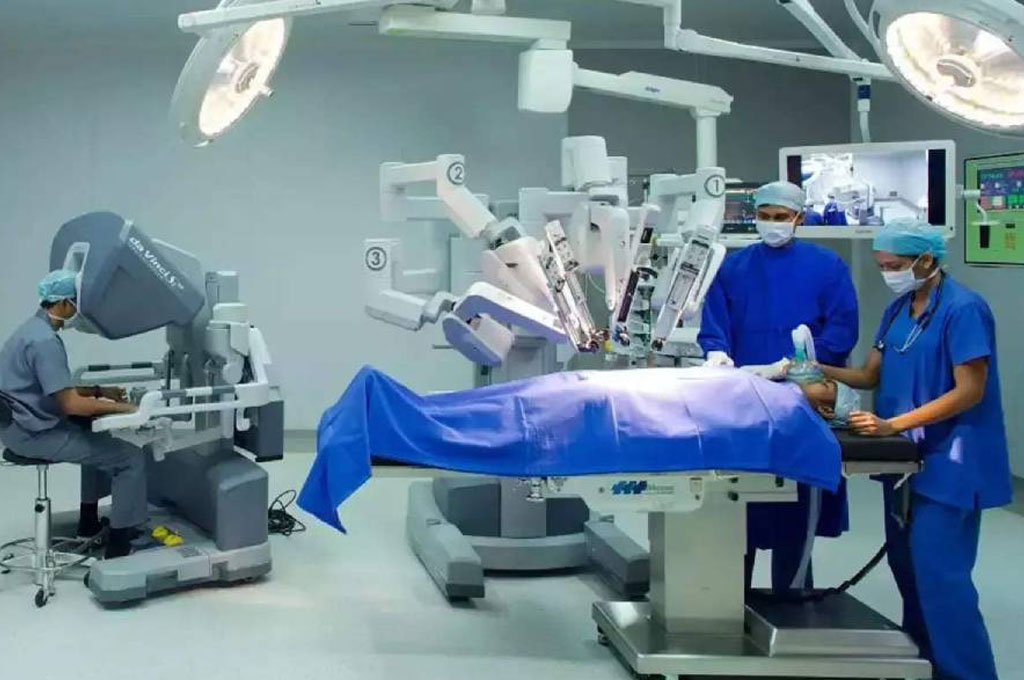
Now widely used for cervical and uterine cancers with several advantages:
Radical hysterectomy with pelvic lymph node dissection
Sentinel lymph node biopsy in select cases
Precision surgery with less bleeding, fewer complications, and faster recovery
Robotic and laparoscopic surgeries offer excellent outcomes with minimal hospital stay and cosmetic benefits.
Don’t wait. Gynaecological cancers are highly treatable—especially when caught early. And with modern surgery, organ preservation, and targeted treatments, long-term cure is possible even in advanced cases.
Surgical Oncologist | Robotic Gynaecological Cancer Surgeon
HIPEC Specialist | Peritoneal Surface Oncologist
Book your consultation today for expert care, cutting-edge treatment, and compassionate guidance.
Contact
