Urological cancers involve organs of the urinary system and include:
Less common types include:
These cancers are more common in men but can also affect women, especially in the case of kidney and bladder cancers.
Risk factors for urological cancers include:
Never ignore blood in urine or persistent urinary symptoms—early diagnosis leads to better outcomes.
Surgery is the gold standard:
Done via laparoscopic or robotic approach for faster recovery and precision.
Non-Muscle Invasive (Early Stage)
Muscle-Invasive (Advanced Stage)
Urinary diversion options:
For those wishing to avoid stoma, Tri-Modality Treatment (TMT) is an option:
Maximal TURBT, followed by chemo + radiotherapy to preserve the bladder
Early stage (selected cases): Robotic/Laparoscopic prostatectomy
Advanced stage: Managed with:
Treatment is customized based on age, fitness, and cancer stage.
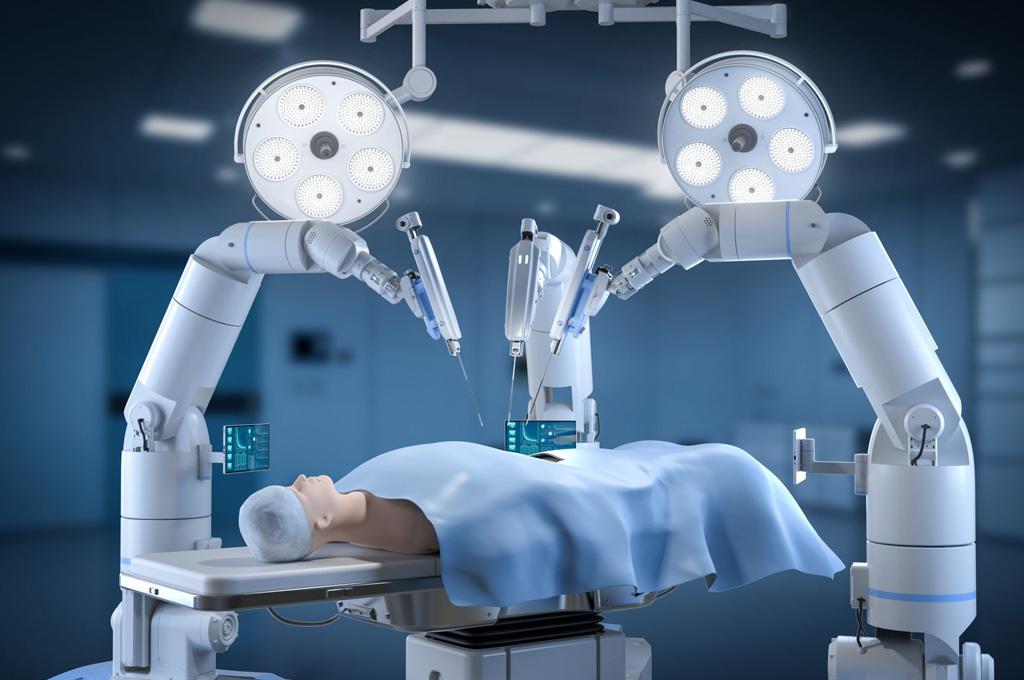
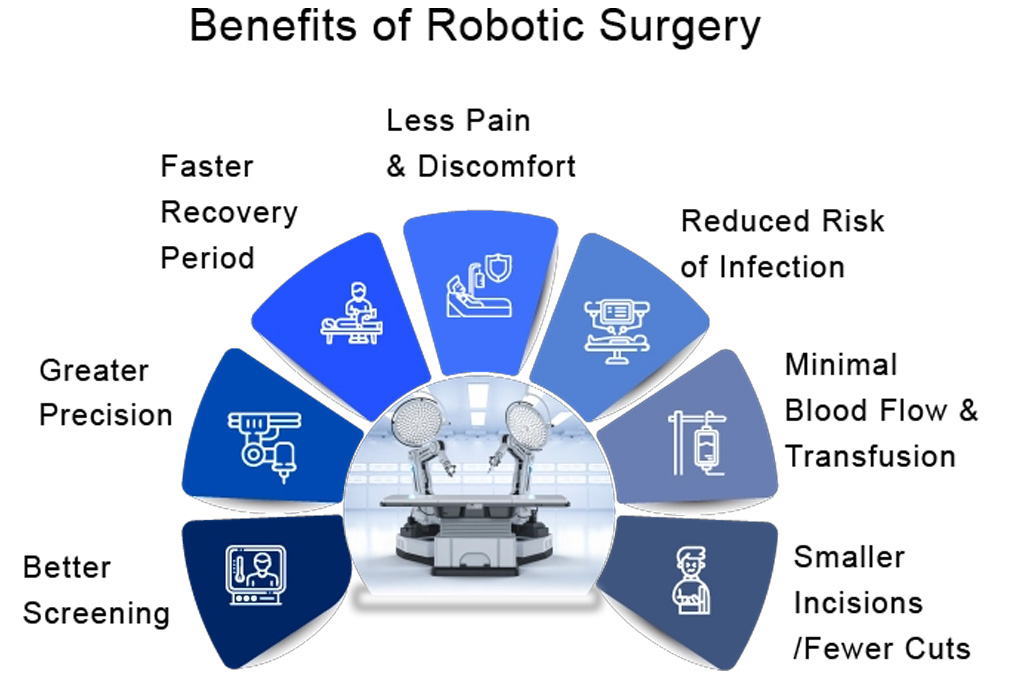
Don’t delay expert evaluation. With early diagnosis and precision surgery, most urological cancers are highly treatable.
Surgical Oncologist | Uro-Oncology Specialist
Robotic Surgeon
Focused on Organ Preservation and Functional Recovery
Book your consultation today to discuss the most advanced and least invasive treatment options.
Contact
